
 - MHz Crystal- 32.768kHz Crystal
Crystal Oscillator List
- MHz Crystal- 32.768kHz Crystal
Crystal Oscillator List
 - Oscillator (CMOS)- Oscillator (Differential)- VCXO- TCXO- OCXO- 32.768kHz Oscillator
Crystal Filter List
- Oscillator (CMOS)- Oscillator (Differential)- VCXO- TCXO- OCXO- 32.768kHz Oscillator
Crystal Filter List
 - Monolithic Filter
Ceramic Device List
- Monolithic Filter
Ceramic Device List
 - Ceramic Resonator- Ceramic Filter
SAW Device List
- Ceramic Resonator- Ceramic Filter
SAW Device List
 - SAW Resonator- SAW Filter
MEMS Oscillator List
- SAW Resonator- SAW Filter
MEMS Oscillator List
 - Low Power MEMS- Differential MEMS
- Low Power MEMS- Differential MEMS



All About Crystals
News > All About CrystalsAfter the growth of quartz crystal blanks is completed, these are cut into quartz crystals of different sizes and thicknesses. However, quartz crystals have different performance characteristics when cut in different types. Among them, AT cutting and BT cutting are commonly used in resonator and oscillator products, while SC cutting are commonly used in OCXO constant temperature crystal oscillators. In this article, we mainly introduce the comparison between AT cutting and SC cutting.
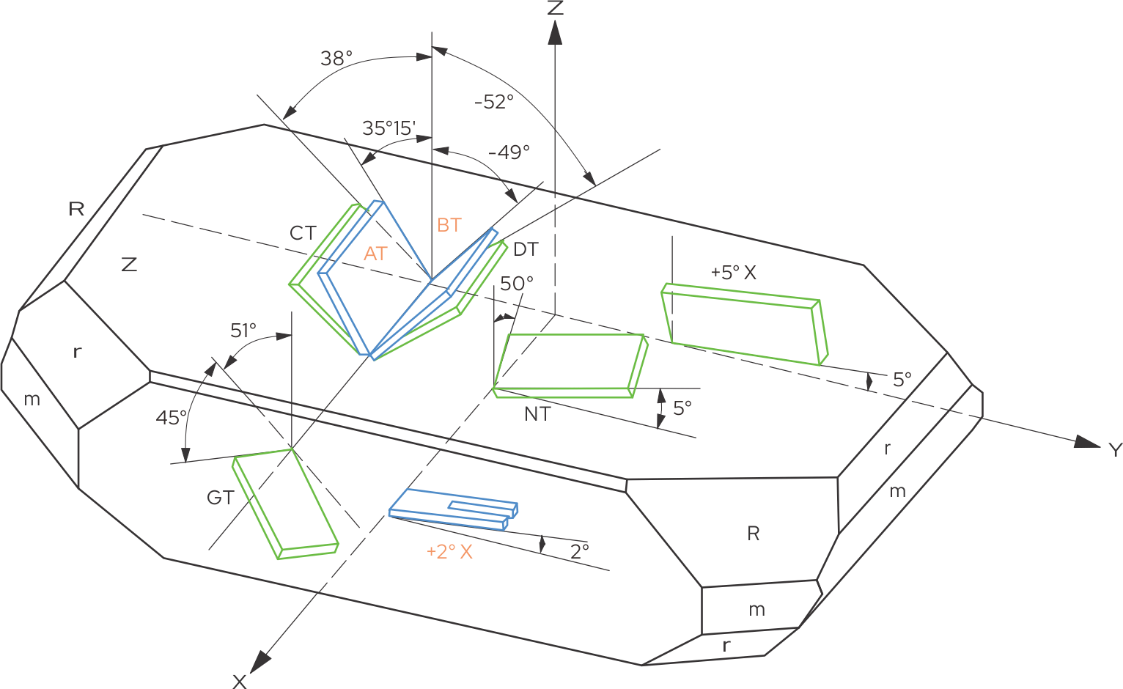
Quartz block with all different cuttings.
We can see from the above figure that the AT cutting method rotates from the Z-axis 35° to the Y-axis direction. It has good performance over a wide temperature range and is symmetrical around 25°C (known as the inflection point temperature). An angle with good stability can be generated within the temperature range of -55°C to 125°C. BT cutting, on the other hand, cuts in the 49° direction of the Z-axis, and both types of cutting methods have the same vibration mode (thickness shear).
SC cutting is a stress compensated cutting, with a turning point temperature of about 92°C, but it is also temperature compensated. SC cutting was originally developed in 1974 as a dual rotation cutting (similar to composite oblique cutting in woodworking), defined as Theta=34.11° and Phi=21.93 °. Due to the anisotropy of quartz crystals, the stress observed on the AT section can be reduced or eliminated by performing a second rotation in the Phi direction.
The working frequency range of AT cutting is 0.5~300 MHz
BT cutting is also the same, ranging from 0.5~200 MHz
The working frequency range of CT cutting is 300~900 kHz
The working frequency range of DT cutting is 75~800 kHz
XT cutting, this type of cutting is used for low-frequency operations. Its range is 5~100kHz. A common frequency used is 32.768 kHz.
GT cutting, this type has an angle of 51°. Its frequency range is 0.1~2.5 MHz
IT cutting is similar to SC cutting type. Its operating frequency range is 0.5~200 MHz
The key parameters between AT cutting and SC cutting are frequency and temperature stability, crystal aging, gravity sensitivity, initial frequency accuracy, availability, and cost.
When working in the high-temperature range (-20°C~+200°C), SC cutting can provide better frequency and temperature stability performance. At a turning point temperature of approximately 90°C (compared to the 25°C cut by AT), SC will achieve stricter stability within these ranges. Within this extended temperature range, the improvement may be up to 5 times higher.
SC cutting is less sensitive to certain effects of aging, such as crystal mounting stress, crystal blank coating stress, and changes in electronic device performance. The G-sensitivity of SC cutting is also lower than that of AT cutting. Low G-sensitivity is crucial for applications that will experience large vibrations and impacts.
We have compared the differences between AT cutting and SC cutting in various performance parameters in the table below.
AT-Cut | SC-Cut | |
Temperature Stability | Good | Excellent (<10 ppb) |
Aging | Good | Excellent (<2 ppb/day) |
Drive Level Sensitivity | Good | Excellent |
G-Sensitivity | Good | Excellent |
Frequency Offset | Good | Excellent |
Availability | Excellent | Good |
Lead Time | Fast | Normal |
Cost | Low | High |
Q-Value | Lower | Higher (Able to achieve low phase noise) |
Working Frequency Range | 0.5~300 MHz | 0.5~200 MHz |
Mode | Shear Vibration | Shear Vibration |
AT-cut and SC-Cut Characteristics Comparison